1 min. read
·Laws and regulations
Laws and regulations to
achieve climate goals
In 2015, 195 countries signed the Paris Climate Agreement. The core of the agreement: limit global temperature rise to a maximum of 2 degrees Celsius by 2050, with an aspirational target of 1.5 degrees. The legislation stemming from the Paris Agreement is complex and constantly evolving. Ecommit keeps track of these developments and explains what the (upcoming) laws mean for your business.

Information provision
The role of ecommit
At ecommit, a team of legal experts closely monitors developments in current and upcoming carbon dioxide legislation. As specialists in carbon offsetting, we consider it our responsibility to provide businesses looking to address their carbon emissions with accurate and up-to-date information. We regularly send out newsletters covering legal updates, and we write blogs and whitepapers that clarify and explain legal topics in a practical way. Of course, we also offer ongoing advice to our clients after they purchase carbon credits, such as guidance on how to communicate sustainability claims effectively.

Reporting requirement
What is the CSRD?
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is a European law that mandates companies to report on their sustainability performance and operations. The obligation applies to listed and large companies that are required to report on their 2025 financial year. It therefore also affects the (SME) suppliers with which these companies work. Even if your company is not yet required to comply with the CSRD, it is wise to familiarize yourself with it and start preparing now.
Read the whitepaper on the CSRD
Carbon offset essential to meet temperature goals
Research by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) indicates that reducing carbon emissions alone will not be enough to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius. To achieve this temperature goal, it is also essential to remove carbon from the atmosphere.
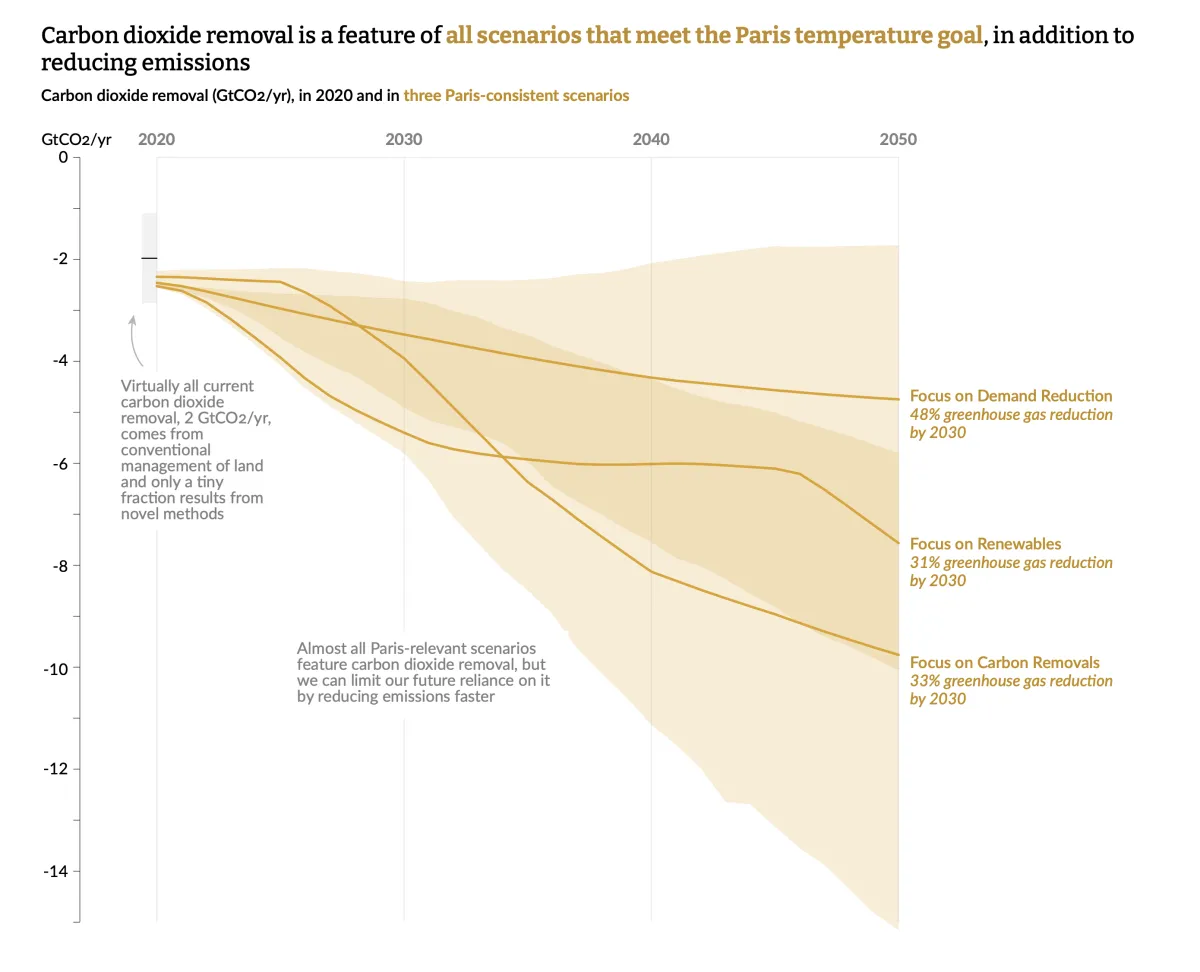
Source: The State of Carbon Dioxide Removal (2023)

Certification requirements
What is the CRCF?
The EU Carbon Removal and Carbon Farming (CRCF) Framework is a voluntary regulatory framework that sets requirements for the certification of climate projects that remove carbon from the atmosphere. These requirements aim to promote high-quality carbon removal and prevent greenwashing, which involves making false sustainability claims. By establishing certification standards, the European Union seeks to build trust in carbon removal projects and incentivize farmers to develop initiatives that provide an additional income stream through the sale of carbon credits.
Read the whitepaper on the CRCF

Due diligence requirements
What is the CSDDD?
The Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) is a guideline for large companies to prevent, end, and mitigate negative impacts on human rights and the environment throughout their value chain. This includes issues like child labor, worker exploitation, biodiversity loss, and pollution. In addition to these due diligence requirements, companies must also develop a plan to align their business models with the goal of limiting global temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Read the whitepaper on the CSDDD

Carbon border tax
What is the CBAM?
The Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) is a tax on the import of carbon-intensive goods from outside the European Union. It is linked to the Emission Trading System (ETS), which requires high-emission sectors to surrender one emission allowance for every tonne of carbon emitted. CBAM aims to prevent companies from relocating production to countries with no carbon regulations and then importing those goods into the European Union.
Read the whitepaper on the CBAM

Carbon reporting requirement
What is the WPM?
The Work-related Personal Mobility Reporting Requirement (WPM) mandates companies with over 100 employees to track carbon emissions from employee commuting and business travel. By 2030, work-related personal travel carbon emissions must be reduced by 1 megatonne. If the annual reports indicate that this target will not be met, the Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management (IenW) may impose a maximum carbon emission limit on employers.
Read the whitepaper on the WPM

Combating greenwashing
What is the GCD?
The Green Claims Directive (GCD) is a regulation designed to prevent greenwashing - where companies make misleading environmental claims to appear more sustainable than they are. The directive is at an advanced stage, but on June 20, 2025, the European Commission announced that it intends to withdraw the proposed directive. However, this has not yet been formalized, so the future of the directive is currently unclear.
Read the whitepaper on the GCD

Combating greenwashing
What is the AFM's Sustainability Claims Guide?
The Sustainability Claims Guide, developed by the Dutch Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM), aims to combat greenwashing, where companies present themselves as more environmentally friendly or sustainable than they actually are. This guide provides clarity for businesses and organizations in the financial sector that make sustainability claims about their products or services to consumers and investors. The goal is to ensure that sustainability claims are accurate, clear, and not misleading.
Read the whitepaper on the AFM's Sustainability Claims Guide

Combating greenwashing
What is the CDR?
The Code for Sustainability Advertising (CDR*), established by the Advertising Code Foundation, aims to prevent greenwashing in advertisements featuring sustainability claims. The CDR provides clear guidelines for advertisers to evaluate their sustainability claims. The CDR covers all types of sustainability claims, including environmental claims and claims about ethical standards such as animal welfare and working conditions.
* There is also an abbreviation CDR which stands for carbon dioxide removal.
Read the whitepaper on the CDR

European climate goals
What is the Green Deal?
The Green Deal represents the European Union's commitment to translating the global objectives of the Paris Agreement into actionable targets at the regional level. By 2050, the EU aims to become the first climate-neutral continent, with an interim goal of reducing carbon emissions by 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. These ambitious climate objectives are further elaborated in the Fit for 55 package, which includes comprehensive legislative measures designed to meet these targets.
Discover all our whitepapers here

Climate target 2040
What is the EU climate target for 2040?
The European Union's climate target for 2040 is to reduce net carbon emissions by 90% compared to 1990 levels, with 5% of this reduction to be achieved through carbon credits. This means that the EU must reduce emissions by 85% and that 5% of the reduction may be achieved through the use of carbon credits. The use of carbon credits will be possible from 2031.
Stay informed with our blogs
In our blogs, you will find everything you need to know about carbon offsetting. We keep up with legislation, provide the latest news, summarize research findings, and share whitepapers.
2 min. read
·2 min. read
·





Carbon emissions
There are many ways to reduce your company's carbon footprint. How much carbon does your company currently emit? What options are available to you? Our information will help you make informed choices.

Carbon offsetting
We collaborate with projects that offset carbon emissions. Are you looking for ways to make your business more sustainable? Contribute to a climate project and receive carbon credits as proof.
Questions about addressing carbon emissions?
Do you have a question or do you want more information? Contact us for a free consultation.


